Ty Robinson
Ty (he/him) started his career in the wine and spirits industry 14 years ago right here at France 44! He took some time away to get a Masters in Gastronomy and since, has worked in every facet of the industry, from restaurants to retail. Ty is a Certified Sommelier by the Court of Master Sommeliers of America. He returned to France 44 in the Fall of 2023 and is happy to have been welcomed back. His favorite wines are Chenin Blanc, Syrah and anything from Germany or Austria.
So you think you hate Chardonnay… So did I. Chardonnay is a grape that has no one true “style.” It’s a chameleon in the wine world. It can range in style from enamel ripping acidic to rich, luxurious and buttery. I feel like Americans have a skewed vision of Chardonnay because here in The States, we have become known for the big rich buttery popcorn laden Chardonnays that our moms all drank growing up. But that is only the beginning of the story for Chardonnay.
Chardonnay is one of the most famous varietals in the world, and rightfully so. It can really be made in so many styles that there is one that will certainly suit you. I always thought I hated the varietal until I came back to the store and have been able to taste different iterations and styles of the grape. I have since come to love the varietal and differences between the many styles of Chardonnay.
Chardonnay is grown across the globe with the main producers being France (Burgundy) and the USA (California and Oregon mostly). What makes Chardonnay unique is the the way winemakers can stylistically manipulate the grapes to produce a range of expressions.
Within Burgundy, you can see bright high acid fruity expressions with no oak (Chablis) AND rich, oily and textural versions that have almost a honeyed tropical fruit note (Meursault).

The story is similar stateside, where our classic California Chardonnays range from rich and buttery, reminiscent of movie theater popcorn, to unoaked varieties that are bright and zippy, with driving acidity and minerality.
Oregon chardonnays tend to be more like Burgundy as they can’t get quite the same level of ripeness as in California, and they generally utilize oak in their winemaking with a lighter hand.
Through all our wine team tastings, I have found that I love unoaked Chardonnay or Chardonnays that use oak in a well-integrated, not overbearing manner. Recently I have been loving the Alois Lageder Gaun Chardonnay from Italy. It sees some oak but it’s there for structure and imparts no flavor components to the wine. Beautifully bright and acidic with aromas of apple and lemon peel, this Chardonnay is light and easy to drink with enough complexity to keep you coming back for another sip.
I also have been loving the Martin Woods Chardonnay. The winemaker lets the purity of the fruit shine through and uses minimal oak (and what he does use is neutral) to create a wine that is reminiscent of Chablis. Bright, fresh, high in acid and a lovely mineral tone to keep the wine zippy.
For oaked Chardonnay, my favorite of late has been the Becker “Schweigener” Chardonnay from the Pfalz in Germany. This Chardonnay is big and bold, much like its California brethren, but it uses oak only to create a rich, mouthfeel and a creamy texture. Beautiful, lush and well made, it made me appreciate what oak can do for Chardonnay.
So get out of your comfort zone – pick up a bottle of Chardonnay and learn about the diverse wines this grape can produce!
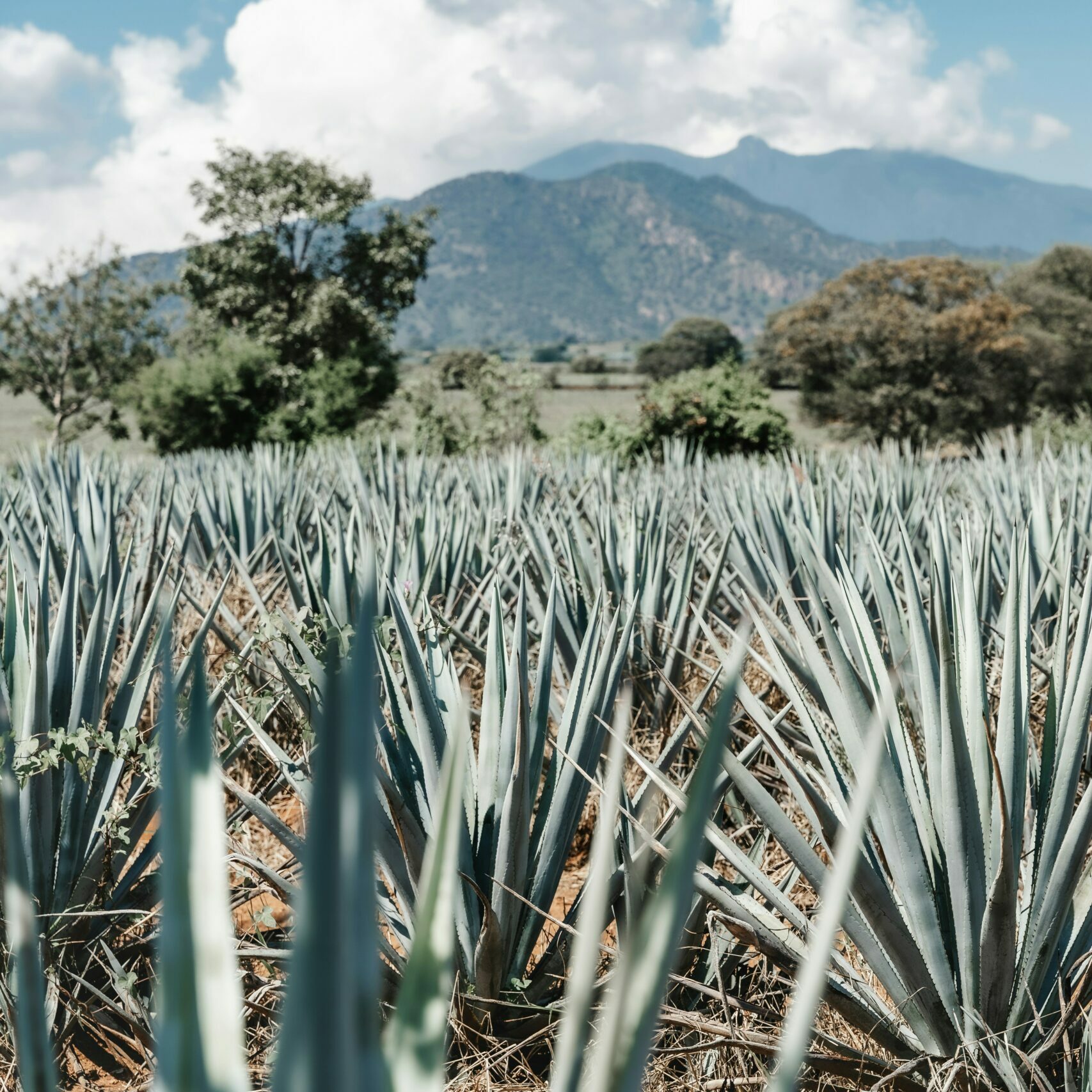


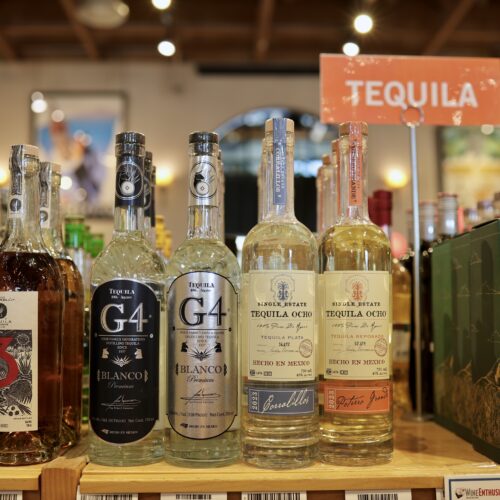
 Additives have been used in tequila since the mid 1800’s when agave plants suffered a blight that was producing faulted tequila.
Additives have been used in tequila since the mid 1800’s when agave plants suffered a blight that was producing faulted tequila.  contribute flavors that are generally added to the tequila through the barreling process. If you’re drinking a blanco tequila, which can only be left in oak for a maximum of 60 days, and you get strong vanilla notes, that’s usually a good sign that oak extract is present.
contribute flavors that are generally added to the tequila through the barreling process. If you’re drinking a blanco tequila, which can only be left in oak for a maximum of 60 days, and you get strong vanilla notes, that’s usually a good sign that oak extract is present. 